DETECT TRANSTHYRETIN AMYLOID
CARDIOMYOPATHY
檢測轉甲狀腺素
DISCOVER THE TOOLS TO DIAGNOSE
SEE HOW NUCLEAR SCINTIGRAPHY, EMB, AND GENETIC TESTING CAN SUPPORT AN EARLY

EVIDENCE FOR NUCLEAR SCINTIGRAPHY
核子閃爍攝影檢查的相關實證
When ATTR-CM is suspected, diagnosis can be made noninvasively with nuclear scintigraphy and testing to rule out AL amyloidosis1,2
Nuclear scintigraphy with
- Studies comparing
99mTc-PYP scintigraphy with EMB found that bone radiotracers have avidity for ATTR deposits, whereas avidity for AL cardiac amyloid deposits is minimal or absent3 - Nuclear scintigraphy may identify ATTR deposits early in the course of disease3
- The mechanism for the differential uptake in ATTR vs AL cardiac amyloidosis is unknown, but it has been suggested that the preferential uptake by ATTR may be the result of higher calcium content3
Sensitivity and specificity of nuclear scintigraphy for ATTR-CM
- A multicenter international study of scintigraphy at amyloid centers of excellence demonstrated 100% specificity for
ATTR-CM using visual grade 2 or 3 with concurrent testing to rule out AL1
NUCLEAR SCINTIGRAPHY USING BOTH PLANAR AND SPECT IS A NONINVASIVE, READILY AVAILABLE DIAGNOSTIC TOOL WITH HIGH SENSITIVITY AND SPECIFICITY FOR
MULTISOCIETAL EXPERT CONSENSUS RECOMMENDATIONS FOR DIAGNOSING ATTR-CM WITH NUCLEAR SCINTIGRAPHY3*
使用核子閃爍攝影檢查於診斷 ATTR-CM 的共識建議3*
DIAGNOSING
IMAGING
The role of
99mTc-PYP has avidity for cardiac amyloid deposits3- Images can be scanned early (1 hour) or late (3 hours)3
- Interval between injection and scan3
- Both planar and SPECT imaging should be reviewed and interpreted using visual and quantitative approaches irrespective of the timing of acquisition3
INTERPRETATION
2-step interpretation of
Step 1: Visual Interpretation
- Visual interpretation should include an evaluation of planar and SPECT images to confirm diffuse radiotracer uptake in the myocardium3
- SPECT imaging can be used to differentiate myocardial radiotracer uptake from residual blood pool activity, focal myocardial infarct, and overlapping bone (eg, from rib hot spots from fractures). Recommend repeating SPECT at 3 hours if excess blood pooling is noted at 1 hour3
- If myocardial tracer uptake is visually present on SPECT, proceed to step 2, semiquantitative grading3
Step 2: Semiquantitative Grading
There are 2 approaches to performing semiquantitative grading3:
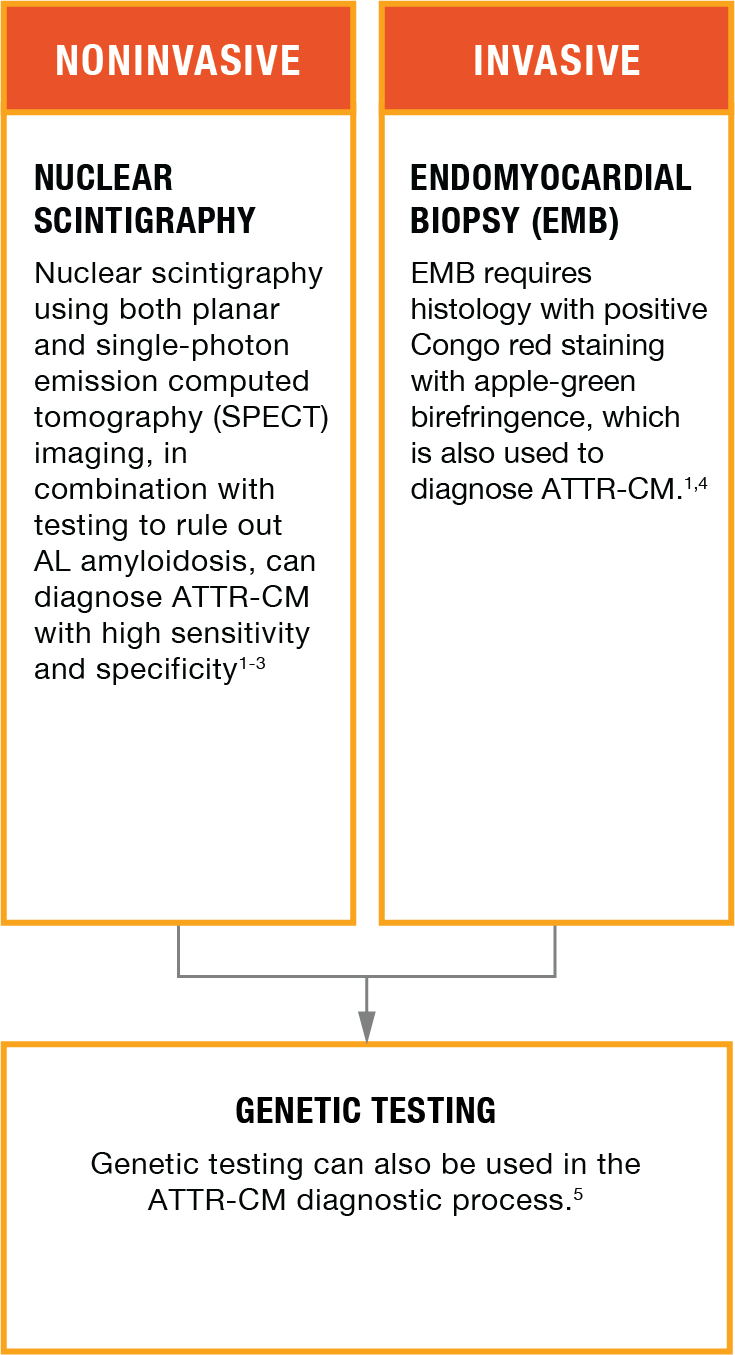
1-hour approach: heart-to-contralateral lung (H/CL) ratio at 1 hour (validated for
 Positive uptake
Positive uptake
 H/CL = 1.86
H/CL = 1.86
Illustrative representation.
H/CL RATIOS OF ≥1.5 AT 1 HOUR CAN ACCURATELY IDENTIFY ATTR CARDIAC AMYLOIDOSIS IF SYSTEMIC AL IS RULED OUT.3
3-hour approach: visual comparison to bone (rib) uptake at 3 hours3,6
 Grade 0
Grade 0
 Grade 1
Grade 1
 Grade 2
Grade 2
 Grade 3
Grade 3
 No myocardial uptake and normal rib uptake
No myocardial uptake and normal rib uptake
 Myocardial uptake less than rib uptake
Myocardial uptake less than rib uptake
 Myocardial uptake equal to rib uptake
Myocardial uptake equal to rib uptake
 Myocardial uptake greater than rib uptake with mild/absent rib uptake
Myocardial uptake greater than rib uptake with mild/absent rib uptake
Illustrative representation.
WHEN CARDIAC AMYLOIDOSIS IS SUSPECTED, GRADE 2 OR 3 MYOCARDIAL UPTAKE (PLANAR AND SPECT), WITH CONCURRENT TESTING TO RULE OUT AL, IS DIAGNOSTIC OF
*Written by a writing group of experts in cardiovascular imaging and amyloidosis assembled by the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology and endorsed by 9 societies including the American College of Cardiology, American Heart Association, American Society of Echocardiography, European Association of Nuclear Medicine, Heart Failure Society of America, International Society of Amyloidosis, Society of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, and Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
†Rule out AL: testing for presence of monoclonal protein via serum and urine immunofixation (IFE) and serum free light chain assay.1
EMB—AN INVASIVE APPROACH TO DIAGNOSE ATTR-CM
心肌組織切片檢查 (EMB) - 診斷 ATTR-CM 的一種侵入性方法
Congo red staining of myocardial tissue on light microscopy and apple-green birefringence on polarized light microscopy images

Congo red positive for amyloid myocardial biopsy image
Image courtesy of Filiale d’Imagerie Cardiovasculaire.

Apple-green birefringence myocardial biopsy image
Illustrative representation rendered from image courtesy of Filiale d’Imagerie Cardiovasculaire.
- To determine amyloid type, immunohistochemistry (IHC) tests and/or mass spectrometry should be performed1
- Risk of complications and the need for specialized centers and expertise may contribute to a diagnostic delay1,4
GENETIC TESTING—USED IN THE ATTR-CM DIAGNOSTIC PROCESS
基因檢測 - ATTR-CM 診斷過程所使用的工具
- Used to determine if the disease is hereditary due to a mutation in the TTR gene or if it is wild type5
- Genetic counseling and gene sequencing are recommended following confirmation of
ATTR-CM 5
A DIAGNOSTIC APPROACH
診斷流程
FOR PATIENTS WITH SUSPECTED CARDIAC AMYLOIDOSIS THAT INCLUDES TESTING FOR MONOCLONAL PROTEIN FOLLOWED BY SCINTIGRAPHY AND/OR BIOPSY7


Reprinted with permission from Maurer MS, Bokhari S, Damy T, et al. Expert consensus recommendations for the suspicion and diagnosis of transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis. Circ Heart Fail. 2019;12:e006075. doi:10.1161/ CIRCHEARTFAILURE.119.006075 © 2019 American Heart Association, Inc. All rights reserved.
- 99mTc-PYP is a noninvasive radioactive tracer utilized as an adjunct in the diagnosis of
ATTR-CM , though not FDA approved for that use† - Both planar and SPECT imaging should be reviewed and interpreted using visual and quantitative approaches3
*If fat pad is negative, biopsy of involved organ is required.
†Please consult individual labeling for risks.
ATTRm, mutant transthyretin amyloidosis; MGUS, monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging.
MAKING AN ATTR-CM DIAGNOSIS
Watch a cardiologist diagnose
In the previous videos, Dr. Detective had a patient referred to him. He suspected
References: 1. Gillmore JD, Maurer MS, Falk RH, et al. Nonbiopsy diagnosis of cardiac transthyretin amyloidosis. Circulation. 2016;133(24):2404-2412. 2. Bokhari S, Castaño A, Pozniakoff T, Deslisle S, Latif F, Maurer MS. 99mTc-Pyrophosphate scintigraphy for differentiating light-chain cardiac amyloidosis from the transthyretin-related familial and senile cardiac amyloidosis. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013;6(2):195-201. 3. Dorbala S, Ando Y, Bokhari S, et al. ASNC/AHA/ASE/EANM/HFSA/ISA/SCMR/SNMMI expert consensus recommendations for multimodality imaging in cardiac amyloidosis: part 1 of 2—evidence base and standardized methods of imaging [published online ahead of print August 29, 2019]. J Nucl Cardiol. doi:10.1007/s12350-019-01760-6 4. Narotsky DL, Castaño A, Weinsaft JW, Bokhari S, Maurer MS. Wild-type transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis: novel insights from advanced imaging. Can J Cardiol. 2016;32(9):1166.e1-1166.e10. 5. Maurer MS, Elliott P, Comenzo R, Semigran M, Rapezzi C. Addressing common questions encountered in the diagnosis and management of cardiac amyloidosis. Circulation. 2017;135(14):1357-1377. 6. American Society of Nuclear Cardiology (ASNC). ASNC practice points: 99mTechnetium-pyrophosphate imaging for transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis. Available at: https://www.asnc.org/files/19110%20ASNC%20Amyloid%20Practice%20Points%20WEB(2).pdf. © 2019 American Society of Nuclear Cardiology. 7. Maurer MS, Bokhari S, Damy T, et al. Expert consensus recommendations for the suspicion and diagnosis of transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis. Circ Heart Fail. 2019;12:e006075. doi:10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.119.006075
